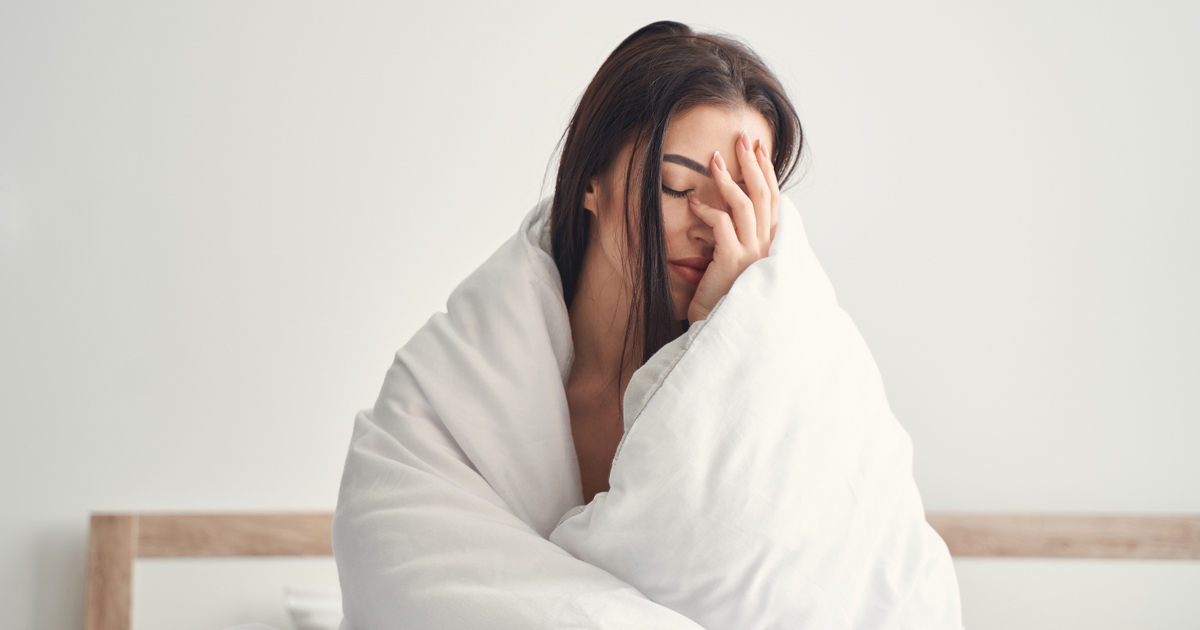

Insomnia: Causes, Symptoms and Solution
Imagine you are lying in bed, staring at the ceiling… The sound of the clock ticking appears louder than ever, and your mind is racing with a million thoughts. You toss and turn in the bed and no matter which side you are on, every posture seems uneasy. The hours pass, causing frustration and anxiety. The question keeps ringing: “Why can’t I sleep?”
Does this sound familiar?
If it does, and that too quite frequently, then you must be careful it could potentially be insomnia!
Insomnia: a sleep disorder that is more common than we even can estimate – hundreds and thousands of people suffer in complete silence.
Far from a sleepless night or two, insomnia can turn bedtime into a battleground. For some, it’s an inability to fall asleep even when completely exhausted; for others, it’s waking up several times in the middle of the night and watching hours tick by. In any case, the result is similar: groggy mornings, slow days, and growing frustration. But insomnia isn’t only about losing sleep, it is about losing the energy, focus, and vitality that good rest brings. It creeps into every aspect of your life – from productivity at work to mood and relationships.
In this article, we’re exploring the meaning of insomnia, what causes it, how to recognise its symptoms, and most importantly, how to fight back. Whether you’re experiencing occasional sleepless nights or chronic sleep deprivation, understanding the root of the problem is the first step toward reclaiming your rest and your life.
So, if you are fed up with being tired, read on. Solutions are closer than you think.
What is insomnia?
Essentially, it’s a simple sleep disorder: an overwhelming chronic inability to fall asleep or stay asleep or both. Of course, far more than lying in bed for hours at night is most often a symptom of deeper imbalances in your body and/or mind.
The meaning of insomnia is not just a few bad nights. Chronic insomnia endures for weeks, months, and even years to disrupt daily life, and be productive, and healthy. Some affected are students, beset by the pressure of meeting deadlines, or adults working and trying to run households and family responsibilities under stress.
While normal is the occasional sleeplessness, insomnia falls into:
Acute Insomnia: Short-term and often linked to stress or a major life event.
Chronic Insomnia: Lasting three or more nights a week for three months or more, possibly requiring treatment. Understanding it as insomnia would be the first step toward conquering it.
Insomnia Symptoms: How to Recognize the Signs
The symptoms of insomnia vary from person to person, but the common manifestations are usually found to be a combination of nighttime struggles and daytime fatigue. Here are some common manifestations that one should look for:
Difficulty Falling Asleep
Do you lie awake to watch the ceiling, even after a tired day? That is one of the main and classic symptoms of insomnia.
Night Wake-Ups
Insomniacs wake up many times during the night, causing a disturbance in their sleep cycle, which prevents easy entry into the deep, restorative stages of sleep.
Waking up too early
For others, the problem isn’t falling asleep but waking up too early hours before their alarm and being unable to drift back off.
Daytime Fatigue and Low Energy
Despite spending hours in bed, poor-quality sleep makes you seem tired, groggy, and unmotivated by the end of the day.
Cannot focus
It takes away your energy but also obscures your focus and memory concerning even the most basic details.
Mood Changes
Chronic sleep deprivation often causes irritation, anxiety, or even depression. This can create a vicious cycle that makes it more difficult to sleep.
Early recognition of these insomnia symptoms will help you take action before it significantly impacts your quality of life.
Why Can’t I Sleep? Common Causes of Insomnia
When you lie awake at night, questioning “Why can’t I fall asleep?” The truth often lies deeper than you realize. Insomnia is a culmination of many intertwined factors, including medical conditions and stress. Here is a breakdown of some common causes.
- Stress and anxiety Stress is one of the major causes of insomnia. Whether it is a looming work deadline, financial issues, or personal conflicts, stress keeps your brain in an alert state, making relaxation almost impossible.
Anxiety worsens this because you keep thinking about the past or the uncertainty of the future. Even worrying about not getting enough sleep may exacerbate insomnia.
- Poor sleep hygiene It involves habits at work or other day-to-day activities and sleeping habits, which are part of the ability to sleep. Using a screen late in the night or having irregular schedules results in damage to the body’s internal clock.
- Medical and Physical Conditions Often, insomnia is associated with other medical conditions, such as chronic pain, asthma, acid reflux, or even hormonal imbalances. In addition, sleep disorders like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can also interfere with your ability to stay asleep.
- Mental Health Disorders These include depression and PTSD. The association works in both ways: sleep exacerbates these conditions, but it also makes falling asleep hard.
- Lifestyle Choices Working late, binge-watching shows, or indulging in alcohol before bed can sabotage your sleep. Alcohol may initially make you drowsy, but it interferes with your sleep cycle, making your rest poor.
- Hormonal Changes Hormonal changes in pregnancy, menopause, or even ageing can influence your natural sleep rhythms. Lower levels of melatonin in older adults, for instance, make falling asleep more difficult.
All of these can help you get started on the way back to reclaiming your nights.
What can you do to aid your sleep: Solutions for Insomnia
Insomnia often compels reaching for the most accessible medication: sleeping pills. Quick fixes can relieve sleep deprivation instantly, but their use can’t lead to long-term resolution. These are ways of how to sleep when you cannot.
- Sleep Hygiene Improvements Your sleep environment and habits make or break your chance of resting. Make the bedroom an undisturbed place: disturbance-free.
- Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet.
- Buy a quality mattress and pillow.
- Blackout curtains or a sleep mask can darken the light.
- Establish a sleep routine It will have consistency as one would sleep and wake at a certain time daily, including weekends, thus helping one’s body to adjust to falling asleep.
- Cut on Bed Time Screen The emission of blue light by phones, laptops, and TVs suppresses melatonin production, hence the difficulty in falling asleep. Try powering off electronic devices at least an hour before bed to signal to your brain that it is bedtime.
- Practice relaxation techniques Relaxation is an art. Especially if stress keeps you awake. Try:
- Deep Breathing: Inhale for four seconds, hold for seven, and exhale for eight.
- Meditation: Concentrate on your breath and guided sleep meditations.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and release each group of muscles to reduce physiological tension.
- Manage Your Diet What you eat can impact how well you sleep. Avoid stimulants like caffeine or nicotine in the afternoon and opt for sleep-friendly snacks such as bananas, nuts, or herbal teas.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) It emphasizes negative thought patterns and behaviours that perpetuate wakefulness. Studies have found that it is one of the most effective treatments for chronic insomnia.
- Use natural remedies Herbs like chamomile or supplements like melatonin can induce sleep. Any new supplement should be consulted with a healthcare provider before use.
- Reduce Napping Although an afternoon nap may be very tempting, long naps interfere with nighttime sleep. If you have to nap, do it for less than 20 minutes.
When to Seek Professional Help
 If lifestyle changes and self-help techniques have not worked, it is probably time to see a doctor. A sleep specialist can diagnose underlying issues and recommend treatments tailored to your needs, from medication to advanced therapies.
If lifestyle changes and self-help techniques have not worked, it is probably time to see a doctor. A sleep specialist can diagnose underlying issues and recommend treatments tailored to your needs, from medication to advanced therapies.
If you want to seek professional help we got you covered. You can book a consultation now to know more about your mental health and how you can make it better.
Seek help before it’s too late: The results of not treating insomnia

Left untreated, insomnia doesn’t just steal sleep from you but also has serious consequences for your physical and mental health, which may include:
- A weakened immune system: Chronic sleep deprivation weakens your body’s defence mechanisms, making you more prone to diseases.
- Heart Risks: Insomnia also leads to developing high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
- Weight Gain: Poor sleep disrupts hunger-regulating hormones, leading to overeating and weight gain.
- Mental Health Deterioration: Insomnia worsens anxiety, depression, and other psychological disorders. This underscores that sleep insomnia should not be taken lightly and should call for treatment if it continues.
The Road to Restful Sleep
Insomnia may seem overwhelming, it is not impossible to overcome. Patience, persistence, and the right approach can help you conquer this sleep disorder and enjoy the restorative rest your body craves. Remember that sleep is a necessity and not a luxury. When next you wake up at 2 am, do not get stressed over it but begin with small, incremental action toward the creation of an environment and habits that promote sleep. By addressing the root causes, practising good sleep hygiene, and seeking professional help if necessary, one could reclaim the nights again by waking up refreshed, energetic, and ready to take on the rest of the day. Sweet dreams await you just need to take the first step.

Leave a Reply